10 Natural Ways to Boost Your Nitric Oxide Levels
To boost your nitric oxide levels naturally, try incorporating nitrate-rich vegetables like spinach, celery, and beetroot juice into your diet. Antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, pomegranates, and dark chocolate can also enhance production. Don’t forget L-arginine and L-citrulline supplements. Staying hydrated with nutrient-infused water is essential, while avoiding processed foods will help maintain levels. Regular exercise and mindful hydration can further support your nitric oxide production. Discover even more effective strategies ahead!
Key Takeaways
- Incorporate nitrate-rich vegetables like spinach, arugula, celery, and beetroot juice to enhance nitric oxide levels and support cardiovascular health.
- Consume antioxidant-rich foods such as berries, citrus fruits, dark chocolate, and pomegranates to improve nitric oxide production and protect it from damage.
- Include amino acids L-arginine and L-citrulline in your diet, as they effectively boost the synthesis and prolong the effects of nitric oxide.
- Stay properly hydrated by drinking at least ten glasses of water daily and consider using citrus-infused water to preserve nitric oxide levels.
- Engage in regular exercise, including aerobic workouts and strength training, to promote nitric oxide release and improve overall cardiovascular efficiency.
How Nitrate-Rich Vegetables Boost Your Nitric Oxide Levels

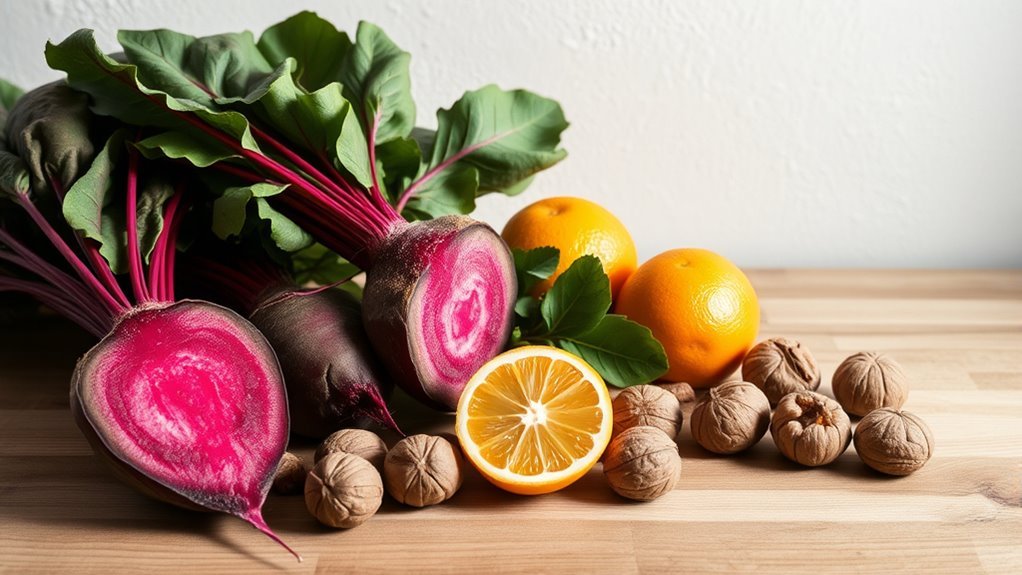
When you incorporate nitrate-rich vegetables into your diet, you’re not just adding color to your meals; you’re actively boosting your body’s nitric oxide levels. Vegetables like arugula and spinach are packed with nitrates, crucial for converting into nitric oxide through your body’s pathways. Just one cup of raw spinach can increase your salivary nitrate levels eightfold, enhancing the benefits. Celery and Swiss chard also contribute by relaxing artery walls and supporting energy conversion. Consuming these greens regularly can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease. Eating these vegetables aids in improving blood flow, which is essential for overall cardiovascular health. Additionally, a healthy diet high in nitrates is necessary for proper nitric oxide production. To maximize these benefits, eat them raw in salads or smoothies, and chew them well to activate the natural processes that turn nitrates into this essential molecule.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods That Boost Nitric Oxide

In addition to incorporating nitrate-rich vegetables, adding antioxidant-rich foods to your diet can further enhance your nitric oxide levels. These nutrient-packed options not only support nitric oxide production but also protect it from oxidative damage.
Consider including these foods in your meals:
- Polyphenol-rich grapes, which improve nitric oxide absorption and release.
- Pomegranates, packed with antioxidants to maintain blood nitric oxide and boost endurance.
- Citrus fruits like oranges and lemons, rich in vitamin C to enhance nitric oxide bioavailability. Green leafy vegetables are also excellent sources of essential nutrients that contribute to overall nitric oxide production, as they are crucial for blood pressure regulation.
- Dark chocolate and red wine, which contain polyphenols that promote nitric oxide production and protect it from breakdown.
L-Arginine and L-Citrulline: Key Boosters for Nitric Oxide

L-arginine and L-citrulline are two amino acids that play crucial roles in boosting nitric oxide (NO) levels in the body. L-arginine is converted into NO by nitric oxide synthase, while L-citrulline helps recycle L-arginine for extended NO production. Notably, L-citrulline is often regarded as superior due to its ability to bypass liver metabolism and inhibit arginase, preserving L-arginine for NO synthesis. Recent research has shown that the ureido oxygen in L-citrulline is derived from dioxygen, highlighting the complexity of NO synthesis pathways. Furthermore, studies indicate that endothelial nitric oxide synthase is critical for producing NO from L-arginine.
| L-Arginine | L-Citrulline |
|---|---|
| Direct substrate for NO | Converts to L-arginine |
| Competes with arginase | Inhibits arginase |
| Decreased bioavailability | Increases plasma L-arginine |
| Less efficient for NO boost | Superior for NO synthesis |
Incorporating both into your diet could markedly elevate your nitric oxide levels.
Hydrate Right: Nutrient-Infused Water Ideas
Boosting your nitric oxide levels isn’t just about amino acids; what you drink can make a significant impact too. Hydrating with nutrient-infused water can optimize your body’s nitric oxide production. Here are some revitalizing ideas to take into account:
Elevate your nitric oxide levels with nutrient-infused hydration for optimal health benefits.
- Beet-infused water: Rich in dietary nitrates, they convert to nitric oxide, supporting blood pressure and reducing inflammation. This is especially important as men age, as maintaining muscle mass and function becomes crucial. Additionally, ecdysterone’s anabolic properties can further enhance muscle growth alongside a healthy hydration strategy.
- H2-infused functional water: Quickly elevates nitric oxide levels and maintains them for hours, thanks to the synergy of molecular hydrogen and nitric oxide. Additionally, studies have shown that hydrogen-rich saline can reduce oxidative stress and improve cognitive function after injuries.
- Citrus-enhanced water: High in vitamin C, citrus fruits protect nitric oxide and improve endothelial function. Strength training is also known to enhance overall well-being, which complements the benefits of these nutrient-rich drinks.
- Nitrate-rich vegetable water: Simple yet effective, these vegetables offer an inexpensive way to boost nitric oxide for cardiovascular health.
Incorporating these drinks into your routine can fuel your nitric oxide levels naturally!
The Negative Impact of Processed Foods on Nitric Oxide
Although you mightn’t realize it, processed foods can greatly hinder your nitric oxide production. These foods, especially processed meats, often contain nitrites that form harmful nitrosamines, increasing your cancer risk. Unlike vegetables that support beneficial nitric oxide production with antioxidants, processed options lack these protective compounds. High levels of saturated fat and salt in fast foods not only promote LDL cholesterol but also create a hostile environment for nitric oxide. This can lead to endothelial dysfunction and reduced bioavailability of nitric oxide. Regular consumption of these items pushes your body into nitrosative stress, resulting in diminished nitric oxide levels. Current research suggests that dietary nitrates and nitrites can be rapidly absorbed and metabolized, yet the health risks associated with them remain inconclusive. Maintaining high nitric oxide levels is essential for oxygen transport throughout the body, underscoring the importance of a healthy diet. Additionally, active recovery techniques like light exercise can help enhance nitric oxide production indirectly by improving circulation.
To optimize your nitric oxide, focus on fresh, whole foods rich in antioxidants instead of processed alternatives.
How Does Exercise Boost Nitric Oxide Levels?
When you engage in regular exercise, you’re not just improving your fitness; you’re also enhancing your body’s ability to produce nitric oxide (NO).
Research shows various effects of exercise on NO levels, including:
- Increased eNOS gene expression in your lungs, which elevates nitric oxide from arginine.
- Significant elevation of NO through aerobic and high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
- Enhanced blood flow via reduced reactive oxygen species during workouts.
- Improved cardiovascular efficiency, leading to better circulation. Engaging in strength training can also contribute to the optimization of your hormonal balance, further supporting NO production. Additionally, consistent HIIT workouts can lead to increased muscle strength and endurance, which can also promote nitric oxide synthesis.
Moreover, studies indicate that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) results in a marked improvement in NO levels in the body. Additionally, regular aerobic training has been shown to especially benefit glycemic control and insulin sensitivity, enhancing overall cardiovascular health.
Whether you’re doing aerobic training or HIIT, your body ramps up NO production, contributing to better heart health and muscle function.
Incorporating Beetroot Juice Into Your Daily Diet
Alongside regular exercise, another natural method for enhancing nitric oxide levels is incorporating beetroot juice into your daily diet. This juice is rich in nitrates, which your body converts into nitric oxide, helping to relax and widen blood vessels. Research shows that drinking beetroot juice increases exhaled nitric oxide levels and boosts plasma nitrate and nitrite concentrations considerably more than nitrate salts. For older adults, regular consumption can lower blood pressure by reshaping the oral microbiome, promoting beneficial bacteria while suppressing harmful ones. Additionally, beetroot juice can enhance exercise performance, reducing oxygen consumption during high-intensity workouts. However, recent studies indicate that beetroot juice may not enhance blood flow during low to moderate-intensity exercise. By including beetroot juice in your routine, you can support ideal nitric oxide production and improve overall health. Notably, it is hypothesized that beetroot juice also possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, potentially working alongside nitric oxide to enhance its effects.
The Health Benefits of Antioxidant-Rich Fruits
Antioxidant-rich fruits can play an important role in enhancing your body’s nitric oxide levels, as they’re packed with essential nutrients that help protect and boost this significant molecule.
Including these fruits in your diet can provide a range of health benefits:
- Citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits boost Vitamin C, managing free radicals and enhancing nitric oxide synthase activity.
- Pomegranates elevate nitric oxide availability, supporting athletic performance while reducing blood pressure. Additionally, maintaining optimal NO levels is crucial for overall cardiovascular health, as dietary nitrates found in fruits can also contribute to increased nitric oxide production.
- Grapes, especially red and purple varieties, contain polyphenols that improve nitric oxide release and circulation.
- Montmorency cherries lower blood pressure and may enhance cycling performance through increased nitric oxide production.
Delicious Nutrient-Dense Smoothies to Boost Nitric Oxide
If you’re looking to naturally enhance your nitric oxide levels, incorporating delicious and nutrient-dense smoothies into your diet is a fantastic choice. Here are some mouthwatering options to contemplate:
| Smoothie Type | Key Ingredients |
|---|---|
| Beet-Based Smoothie | Beets, mixed berries, spinach, pineapple, turmeric |
| Leafy Green Smoothie | Spinach, celery, ginger, garlic, banana |
| Berry & Fruit Smoothie | Berries, pomegranate juice, watermelon, chia seeds |
Try the Nitrate Berry Beet Smoothie, packed with beets, spinach, and berries for an antioxidant boost. Additionally, incorporating nitrates in beets can help enhance blood flow and oxygen delivery to the body, making these smoothies not only delicious but also beneficial for your cardiovascular health. Furthermore, the Nitrate Berry Beet Smoothie is rich in potassium and essential minerals, which supports the maintenance of a healthy weight. Or blend a revitalizing green smoothie with spinach and ginger. With these nutrient-dense options, you’ll enjoy great flavors while boosting your nitric oxide levels naturally!
Key Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Nitric Oxide Production
Incorporating smoothies into your diet is just one delicious way to boost nitric oxide levels. To further elevate your nitric oxide production, consider these key lifestyle changes:
- Exercise regularly: Aim for 20-30 minutes of heart-healthy activities like jogging or cycling. Engaging in physical activity stimulates nitric oxide release, enhancing blood flow and nutrient delivery. Additionally, regular exercise increases endothelial function, which is crucial for maintaining vascular health.
- Practice nasal and deep breathing: This enhances oxygen uptake and circulation while promoting nitric oxide synthesis.
- Stay ideally hydrated: Begin your day with 16 ounces of water and drink at least 10 glasses daily, adding hydrating fruits like cucumber or berries.
- Manage stress: Utilize deep breathing and meditation to support nitric oxide levels and combat chronic stress.
Making these changes can markedly enhance your nitric oxide production, leading to improved overall health and wellness.
Questions
What Are the Signs of Low Nitric Oxide Levels?
If you’ve low nitric oxide levels, you might notice high blood pressure, fatigue, erectile dysfunction, cold extremities, poor exercise performance, memory issues, and sluggish recovery after workouts. These signs can impact your overall health considerably.
Can Nitric Oxide Supplements Be Harmful?
Yes, nitric oxide supplements can be harmful. They can lead to gastrointestinal distress, low blood pressure, or more severe reactions. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation to guarantee safety.
How Quickly Can I See Results From Dietary Changes?
You can often see results from dietary changes within a few days. However, significant improvements in health markers may take longer, generally around one to three weeks, depending on the specific changes you implement.
Are There Any Medications That Affect Nitric Oxide Levels?
“Where there’s a will, there’s a way.” Yes, certain medications can affect nitric oxide levels. For example, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and organic nitrates enhance nitric oxide availability, benefiting conditions like hypertension and angina.
What Is the Best Time of Day to Consume Nitric Oxide-Boosting Foods?
You should consume nitric oxide-boosting foods about 30-60 minutes before exercise for peak performance. Morning or midday is best for general health benefits, but avoid consuming them close to bedtime to prevent sleep disruption.
Conclusion
So, if you want to feel like a superhero zooming through life with supercharged nitric oxide levels, just toss aside processed snacks and embrace those vibrant veggies and antioxidant-packed fruits. Who knew that sipping beetroot juice could have you racing faster than a caffeinated cheetah? Forget about boring diets; it’s a delicious journey of smoothies and hydration. Just remember, your body’s not a science experiment—unless you consider munching on greens a thrilling lab adventure!